Take an exclusive look inside our library of actionable strategy guides, templates, and e-learning modules, covering campaign planning, integrated lifecycle marketing, and managing digital transformation
Our Guides, Templates, Quick Wins, E-learning modules and personalized learning plan are of high quality to help businesses plan, manage and optimize their contribution from digital to multichannel marketing. We cover 7 step strategy guides to actionable templates in Google Sheets, Excel, Word, and Powerpoint.
We deliver briefings on the latest trends and research reports to inform your digital transformation plans. Yet, our core focus isn't top-level research and theory, but actionable best practices for digital channels that directly impact leads and sales.
Our most popular resources, which our competitors don't offer, are actionable templates to audit, forecast and define improvements covering every digital marketing technique. These are field-proven to help our members audit their current performance and identify problems and opportunities to improve results.
For 12 days we will give you a free preview of a different resource, covering in-depth strategy and actionable best practices you cannot miss! Come back every day as we’ll be continuously updating this post to show you more and more winning marketing advice.
Our 12 insights include (more to be revealed each day):
- Day 1. 9 digital marketing megatrends 2018
- Day 2. Digital Marketing Models Guide
- Day 3. B2B digital marketing ebook
- Day 4. RACE elearning module
- Day 5. Integrated Marketing 2020 guide
- Digital Marketing plan template
- Social Media Strategy guide
- Customer retention planning guide
- 10 Business limiting SEO mistakes
- Customer persona guide
- Email Tends 2018: A Visual Guide
- Landing page conversion guide
Day 1. 9 Digital marketing Megatrends 2018
We start the 12 days off by answering one of the most sought-after answers this time of the year: “What trends in marketing are likely to have the biggest impact for my business in 2018 and beyond?”
Take a look inside:

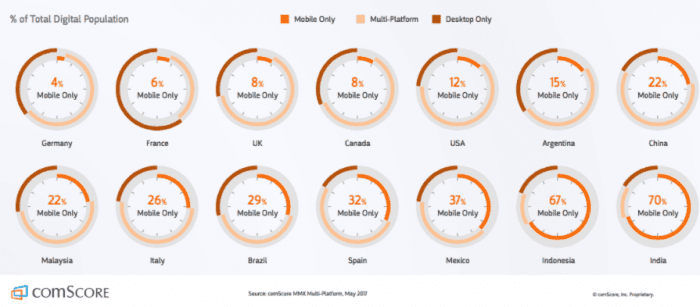
Megatrend 1. Skyrocketing smartphone adoption
The growing importance of mobile marketing and apps is shown by these stats (Source: Smart Insights Mobile Marketing Trends statistics compilation)
- More than 50% of searches are on mobile
- 91% of Facebook usage (Daily Active users) is on mobile
- 80% of Facebook advertising revenue is on mobile
- 90% of mobile media time is spent in apps
The importance of mobile platforms is shown in this interesting visual from comScore. It suggests that rather than following Google’s ‘Mobile-First’ mantra, most businesses need to develop a multichannel or multiplatform strategy to engage consumers across mobile and desktop
Megatrend 2. Increased use of Conversational UIs
Gartner feature Conversational User Interfaces as one of the emerging technologies on their hype cycle which we feature later in this article. We define the scope of Conversational UIs to include:
- 1. Chatbots. We featured several examples of these in 2017 which run on proprietary platforms. Marketers should also consider integrating with standard platforms for customer service or pre-sales support, for example, Facebook’s Bot Engine for Messenger, which went live in April 2016 when Google also announced its assistant service at Google I/O.
- 2.Software and human-assisted support. Human-assisted live chat has existed for some time. What is new here is the addition of segmentation and automation rules to trigger messages on site, in-app or through email via technologies like Intercom, Helpcrunch and Drift. These offer not-only service, but can also support sales and audience engagement and are a great fit for smartphone use.
- 3.Voice controlled search assistants. Voice controlled searches are rising and likely you’ll know about Apple’s Siri, Microsoft’s Cortana, Amazon’s Alexa and Google’s Assistants which can be used on smartphone,
- 4.Voice controlled connected devices. Adoption has been boosted by advertising from Amazon for its Echo devices and Google’s Home devices launched in October 2017.
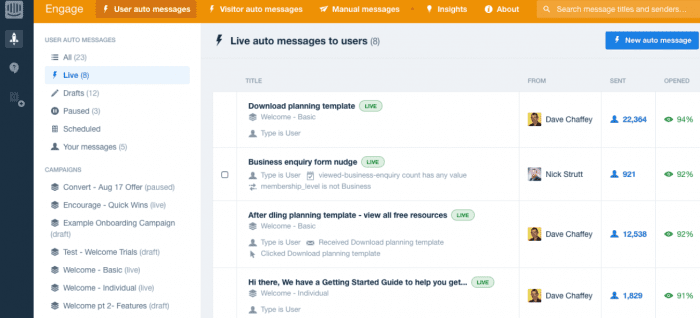
For most businesses, 1 and 2 are going to be of most practical application. It will be interesting to see how Chatbots prove to be, to end users. We’re certainly excited by the potential of Intercom, here is an example from our instance showing rules we have set up to trigger messages in real-time suggesting content to members. These give far higher response rates than email since they don’t suffer from inbox competition and are in the context of a website visit.
Online publisher TechCrunch has noted the trend in Chatbot use, saying that Chatbots have suddenly become the biggest thing in tech, explaining that they promise to:
“Unlock the ability to provide personalised, interactive communication akin to talking to a human customer service or sales rep, but at scale for much cheaper than call centres”
From Facebook’s Mobile Messenger through Facebook’s acquisition of WhatsApp and rebuff by Snapchat to the popularity of apps in non-Western markets like WeChat, there is a continued and growing wish for consumers to communicate directly outside of public social network pages. This is really the last frontier for social media monetization, so we can expect to see some major changes here in 2018 with new options for paid media on messaging apps, although this will be limited since the app owners have committed in the past to keeping messaging ad-free.
So, reaching and influencing consumers as they move from public social media to messaging will remain a challenge to businesses, but as this next trend shows, there will be new options for reaching consumers via messaging.
Download FREE Resource – 9 Digital marketing megatrends 2018
Megatrends across the 5 pillars of marketing today which every business should action.
Access the
Day 2. Digital Marketing Models Guide
We have created this guide based on the growing need for a definitive source of digital marketing models. We have started with the top ten and it may be that there are others you think we should include in the next version.
As with our Essential Marketing Models, this guide explains the fundamentals of each model, how it works and gives examples of how to use each model along with best practice advice and templates to use in your business.
Take a look inside:

Model 5. 6Cs of online customer motivation
What is it?
The 6Cs of motivation is a recognized tool used in higher education and looks at ways to improve classroom motivation and student participation. In 2004 Dave Chaffey suggested the 6Cs of customer motivation in a world where the online offer was developing. The aim was that a model of customer motivation would help define the Online Value Proposition
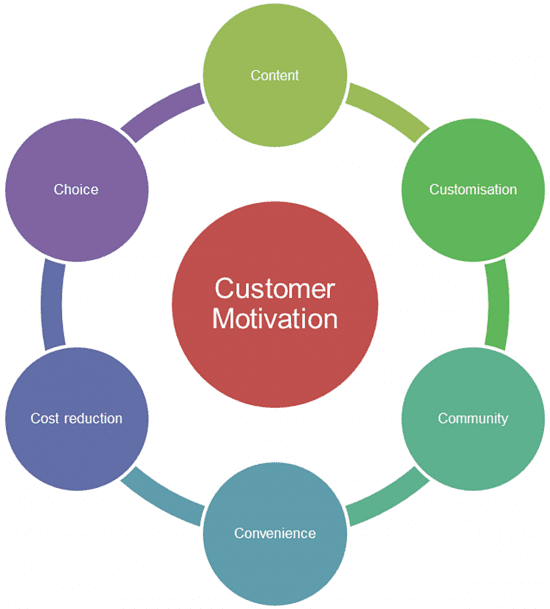
How can I use this model?
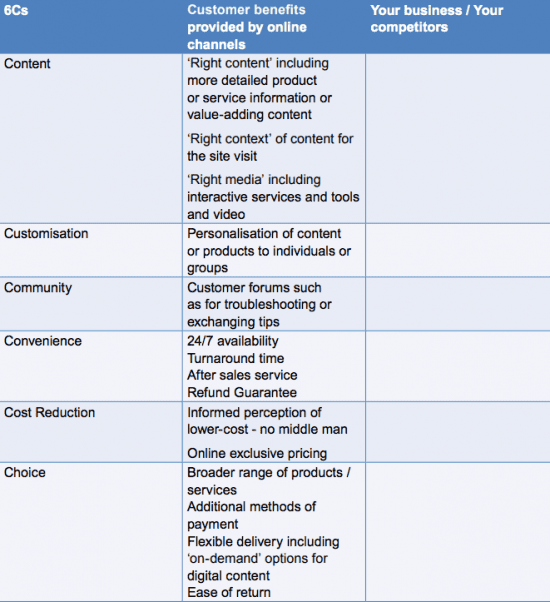
The 6Cs provide clarity when building or refining a website. You can use the template below to assess the benefits a website and online services offers online audiences, as well as those of your competitors.
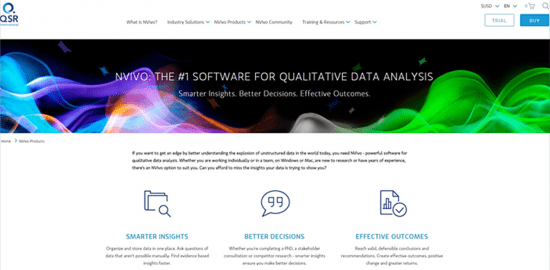
Looking at an example, I am considering buying some data analysis software and searches take me to the QSR website:
Content
The QSR website seems to contain the right content and the right context “The #1 software for …’ The media used includes a strong visual image with additional icons which are clear and simple to understand.
Customisation
Personalisation according to individuals or groups is not clear on this site. It may be that I need to delve deeper to experience customization.
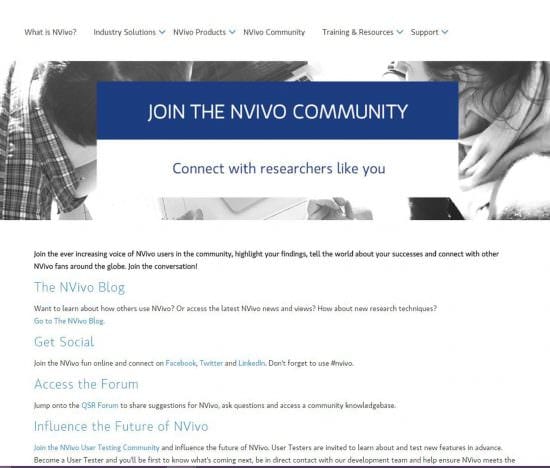
Community
QSR promotes its community spaces on a dedicated page which include options to join as a beta tester ‘to learn about and test new features in advance’.
Convenience
The software is available for immediate download as well as the option of a free trial.
This provides 24/7 availability and the trial is the initial guarantee. After sales service is provided via ‘Support’ and the community space.
Cost Reduction
The element considers the informed perception of lower-cost, as there is no middle man and with an online store, costs may be lower. For this software, it is not entirely relevant, as it cannot be purchased elsewhere.
The concept of cost reduction is an issue where a product is available from several places and if the only perceived difference is the price, customers may seek the goods elsewhere.
This is a major issue in the ‘grey market’ where larger retailers or wholesalers buy goods and sell for less than the recommended retail price. It is also an issue where fake goods are sold via online marketplaces. Customers see such a great price difference, without realizing the items may be copies.
Choice
The QSR website provides choices and helps the customer decide which product is right for them with ‘click here’ boxes.
What to watch for:
If the product or service is not available in other locations or through third parties, the cost reduction element may not be relevant.
Original Source
Source:
Chaffey, D. (2004). E-Business and E-Commerce Management. Pearson Education UK, Harlow. (This book was republished every 3 years since this time, now named Digital Business and E-commerce management).
Download FREE Resource – Digital marketing models guide
Frameworks and mindtools to create digital audits, strategies and plans.
Access the Digital marketing models guide
Day 3. B2B Digital Marketing ebook
An introduction to all the areas you need to review to take your online marketing to the next level. We show you how to create a plan or simply work through all the issues you need to think about to make online B2B marketing more effective. This sample Ebook contains a selection of tools and research taken from the 200 page Brilliant B2B Digital Marketing Ebook.
What does the Ebook include?
- Step 1. Strategy for B2B digital marketing. What needs to go into your plan and why?
- Step 2 Effective websites. What are the requirements for a persuasive B2B site.
- Step 3 Search marketing. Tips on attracting more visitors through SEO.
- Step 4 Content and inbound marketing. Reviewing the best content types for you.
- Step 5 Social media for B2B marketing. How to best use social media for B2B.
- Step 6 Lead generation and E-CRM. Using landing pages to boost leads.
- Step 7 Analytics and improvement. Metrics to use to enhance performance.
Take a look inside:

Lead generation and E-CRM
Q. Has the strategy for online lead generation and follow-up been defined?
Our focus in the last two sections is to assess how a B2B marketer sets about delivering quality leads to the sales team and uses a variety of tools and techniques to drive more, and better quality leads which can be nurtured through to transaction.

The three most common types of landing page for B2B companies are outlined below.
Option 1: Landing page/s integrated into site architecture and style
Most websites are built to facilitate the easy adding of new and additional pages so it makes most sense to create campaign landing pages within the main site as part of the main architecture. The positives are the simplicity – tapping into existing structure, page templates and layouts – and control. The downsides are the need for specific optimization as they are not a micro-site in their own right and they may struggle to convert traffic directly from referrers or from browsers on the main site. We look at many examples and best practices in the Brilliant B2B Marketing guide.
Option 2: Bespoke landing pages that are not part of the main site structure or style
If you are looking for a more ‘stripped down’ landing page that may act to convert traffic from advertising campaigns, or a short-term brand campaign, this is the option for you. Increasingly some B2B companies are looking to differentiate by creating microsites that campaign on a specific issue, which sets them apart and doesn’t necessarily carry the company badge. It also helps some B2B marketers delicately ‘work around’ complicated and embedded corporate websites to provide a campaign solution where one may not be available within the existing site.
Using these types of landing pages in B2B marketing often helps to achieve higher conversion rates whilst delivering a web presence that is more consistent with the overall goals and style of the marketing campaign being activated.
There are some disadvantages – namely that it requires more effort and maintenance and affects user experience across the site (different look and feel, quality and content). Also, to ensure search engine listing, make sure the page/s are incorporated within the same domain.
Again, we look at many examples and best practices in the Brilliant B2B Marketing guide.
Option 3: Micro-sites with several pages or tabbed landing pages
There is an obvious problem with Option 2 in that many visitors to the page will not be at the right point in the buying cycle to convert. The simplicity of running a specific landing page within the architecture of your website that follows the look and feel of the campaign will often increase single visit conversion rates, but it probably caters for the visitors that need more information because they are in ‘buying mode’.
Independent micro-sites take the concept of campaigning further, offering an entirely different site where you can operate more freely in terms of design, tone, message and more. Without the brand restrictions imposed from the main corporate site, companies can promote specific products and services in a more customer-focused way – assuming most corporate websites are not set up to help customers but rather broadcast what the company is good at!
The upsides are stark. Dedicated content and offers targeting specific customers which can be tracked and traced in minutia. Meaning you can categorically work out how successful all areas of your campaign are at each point of the process.
Take this approach and you will get sucked in. But be warned – managing an ever growing number of campaign micro-sites creates obvious problems such as managing domain name ownership, expiry, hosting, content, optimisation and analytics.
For businesses operating in multiple sectors or with products that can be grouped together to create application-specific portfolios, like Westlock controls below, micro-sites rather than integrated website landing pages will clearly work best.
Once the form of landing page is agreed on there are many other issues to decide upon that we review in the 7 Steps guide:
- Range and type of content assets
- Best forms of promotion of landing pages through online marketing channels
- Page layout including form of call-to-action þ Data profiling and lead scoring and qualification
- Providing access to a range of resources
- Personalised email sequences used for lead nurturing
- Integration of online and offline (human) contact
Download FREE Resource – B2B Digital marketing Ebook
Learn the factors for success in online B2B marketing. We show you how to create a plan or simply work through all the issues you need to think about to make online B2B marketing more effective.
Access the
Day 4. RACE elearning module
Our CPD accredited RACE planning framework (reach, act, convert and engage) e-learning will help you learn the fundamentals of successful digital marketing and to create a long-term plan to grow your business using the 25 key digital marketing techniques we recommend.
Take a look inside:
ACT- Audience Integration Strategy
What will I learn in this lesson?
In this lesson, you will learn – Lots! Mostly related to increasing leads from your website or social media.
You will learn how to:
- Review and improve the effectiveness of website customer journeys
- Set Goals in Google Analytics (or other measurement solutions) for key site outcomes
- Create a content marketing strategy

We have defined ACT as a separate conversion step since it's so challenging to encourage online audiences to interact online - it's all too easy for contacts to click the back button, do another search or go onto someone else's social status updates!
Without interaction you limit the opportunity for a first-time contact to remember you and generate leads - that's the main aim of ACT.
Introduction to interACTion
In this topic introducing Act you will learn six steps to improve customer interactions
- Task 1. Define site goals and set up analytics tracking
- Task 2. Define audience types and customer data profiling requirements
- Task 3. Define content marketing strategy including lead generation offers
- Task 4. Define Customer journeys and Conversion Paths
- Task 5. Create a landing page plan – also defining the Strategy for customer journeys
- Task 6. Optimise site page templates and journeys

The Act part of RACE Planning is perhaps the least easy to understand. In this introduction, we’ll explain what’s involved and why we think it’s necessary on top of ‘conversion’.
These are the main activities that need to be managed to improve interaction and boost leads that we will review as topics in this unit.

In the ‘Best Practices section’ we’ll present a summary of the detailed guidance in the next two topics in Six Interaction Tasks where we introduce some of the terms.
We’ve developed these Six Interaction Tasks as a recipe to follow when reviewing an inbound or content marketing plan, creating an annual digital plan, or defining a campaign.
To take a higher-level ‘helicopter view’, there are two top-level deliverables from reviewing Act which focus on:
- Improving interactions on the website (where we focus), mobile apps and social networks. These involve creating a better experience for site visitors and reaching goals for marketing outcomes such as leads.
- Improving content quality to encourage more leads and conversions
Ultimately both are involved in increasing leads, giving the opportunity to increase sales.
What is it?
Act is short for Interact or Interaction.
It’s the initial interaction(s) we’re focusing on when a new visitor first arrives on a website or social media company page.
The type of interaction will vary a LOT depending on the type of business, whether it’s a first or repeat visit and the landing page of the site where the visitor arrives. But essentially it’s about getting a visitor to a site to dwell rather than simply bouncing off – so it means getting them on their journey and to interact with content which are the two key topics in this unit.
An interaction may mean finding out more about a company or its products, searching to find a product or reading a blog post, it’s about ‘getting that next click’ that could eventually generate a lead or sale.
Types of interactions
Common interactions on a website or in a mobile app for prospects are:
- Clicking through to the next page through a call-to-action (CTA) or ‘Scent trail’
- Registering with a site or via a landing page form – lead generation is typically the main aim of ‘ACT’
- Adding user-generated content (such as a comment or a review)
- Liking or sharing content
- Liking or following a business
- Completing a deeper interaction such as completing a quiz or game
- Sharing content or following a brand on social networks
Typically these will be achieved on a company website which is the ‘hub’ for campaign activity. However, some can be achieved on other sites – for example, company social networks, partner sites, and media sites. Offline may also be important, for example, with Event marketing.
For retail or transactional sites, there will be specific goals
- Signing up to a newsletter with a first time purchase discount offer, for example, prompted by a pop-up or panel
- Reviewing product details or reviews
- Learning more about the retailer and it’s proposition (trust, delivery and returns option)
- Adding a product to the Shopping cart
The main measures for initial engagement with a site as assessed through analytics are:
- Bounce rate. The percentage of visitors who leave immediately after viewing only one page.
- Duration or dwell time. Measured as Average Time on Page or Average time on site
- Pages per visit. Pages viewed divided by the number of visits.
Common interactions on a social network are similar as you can see by comparing the two:
- Clicking through to view content on a website
- Registering with a company (if possible on the social network)
- Adding user-generated content (such as a comment on a status update)
- Liking or sharing content
- Liking or following a business
- Completing a deeper interaction such as completing a quiz or game
- Sharing content or following a brand on social networks
Recommended best practices
Task 1. Define site micro and macro conversion goals and setup tracking – this is defining the Opportunity
In this step you need to:
- Review marketing outcomes – micro and macro conversions from a site or social network visit. The macro or main conversion goals are the major marketing outcomes: Sales and Leads – easy – but you still need to check you can measure them across channels.
- Select goals for reviewing interaction outcomes. You should define these actions as top-level goals of the funnel in analytics. Goals can include “Viewed product”, “Added to Basket”, “Registered as member” or “Signed up for an enewsletter. Act is also about encouraging participation. This can be sharing of content via social media or customer reviews (strictly, part of Engage).
- Setup and/or review goal tracking in analytics. We will see that the type of goal selected in Google Analytics will vary a lot by sector.
Task 2. Define audience types and customer data profiling requirements
This involves defining or refining Personas and then selecting key data fields to be entered by the users and then used for following up with email marketing messages.
Task 3. Define content marketing strategy including lead generation offers
This involves:
- Content marketing auditing and planning goals
- Audience insight for content marketing
- Ideation – selection of campaign themes, content types and formats to engage
- Content marketing governance
- Content creation
- Content distribution
- Measurement and Evaluation Technique: Define content marketing evaluation framework and techniques
Task 4. Define Customer journeys and Conversion Paths – this is defining the Opportunity
Review current popular entry points and forward paths.
Review Reverse path analysis to see which pages to improve further
Task 5. Create a landing page plan – also defining the Strategy for customer journeys
Identifying the type of landing page and understanding visitor sources to make them work better (depending on the type of site).
Task 6. Optimise site page templates and journeys
You will have many of these page templates or layouts on your site already, but they will need to be optimised to get better results.
These are the typical page template types that need to be optimised:
- Home page
- Product category page
- Product page
- About page
- Offers page
- Lead generation landing pages
- Pop-ups or header / footer bars containing opt-in offer across page types
View the RACE Digital Marketing planning e-learning course here. This requires a Premium membership, either Monthly or Annual membership plan, to access the full CPD accredited e-learning course.
Day 5. Integrated Marketing 2020 guide
Our integrated marketing 2020 guide will step you through 10 success factors which leading companies are deploying today to future-proof their business by creating more effective, joined-up media investments and customer journeys.
Take a look inside, we cover:
- Resource to compete
- Future-proof your business model
- Engaging content-led brand personality
- Multi-channel lifecycle integration
- Insight-driven improvements
- Aligned digital strategy
- Long-term martech roadmap
- Always-on visibility and engagement
- Hyper-targeted real-time media investments powered by Machine Learning
- Agile optimisation to Marketing Excellence

8. Always-on visibility and engagement
In the pre-digital era, marketing activities have been planned in campaign ‘bursts’ around new product launches and promotions. Digital marketing needs a change in mindset so businesses invest sufficient time and budget into ‘always-on’ activities which can be used in an integrated way to maximise visibility and conversion through the customer lifecycle.
What is it? ‘Always-on’ digital marketing activities
Always-on or inbound digital marketing aims to maintain continuous visibility and persuasion and engagement online 365 days a year as consumers and businesses show their intent to buy by searching online for information about products and services using search engines, social media, reviews, comparison sites and their preferred influencers.
Always on activities also include marketing automation to follow-up on those interested through email marketing, messaging, on-site personalization and off-site re-marketing.
Strategy Recommendation: Review and optimize activities across the customer lifecycle
Many businesses haven’t yet adjusted to create an ‘always-on’ marketing machine that uses digital marketing techniques to continuously tap into daily consumer intent. Yes, we will still need campaigns for demand generation and to push promotions, but these need to be balanced against always-on activities which we have seen sadly neglected way too many times.
Audit and optimize your Always-on customer touchpoints
Smart Insights resources are designed to support the trend to always-on marketing activities using the RACE planning system audit and workbook which defines 25 key activities that every business needs.
We recommend you map current and future online AND define ‘always-on’ marketing activities across the lifecycle using . This will help identify activities you may miss out on if you haven’t planned projects to set them up or optimize them, e.g. re-marketing or marketing automation.
Our Persona template and Excel spreadsheet is also a practical tool for defining personas and content mapping across top-to-middle-to-bottom-funnel to ‘operationalise personas’.
9. Hyper-targeted real-time media investments powered by Machine Learning
When using the World wide web for marketing first came to prominence in the mid-1990s, there was much excitement about personalization offering one-to-one communications with prospects and customers. If you were working in marketing at this time you may remember the ‘One-to-one future” by Peppers and Rogers described this future. For many years, this was out-of-reach for the majority of businesses with only the largest pure-plays like Amazon or eBay developing the tech in house to deliver on this. Hell, Amazon even had a ‘Director of Personalization’ back in 2004, how many other businesses can say they had the same focus on digital marketing then or now?!
Today, twenty plus years later, real-time personalization and one-to-one personalization is a reality for any business of any size who has the vision and commitment to use it.
Using insight on audience interaction with your ads from the ad networks and the major ad platforms like Facebook, Google and LinkedIn enables savvy businesses using Real-time Programmatic advertising services direct or via their agency to vary their creative messages and content throughout the customer lifecycle to define best targeting predictive of sale.
Today we need to use these services and our analytics to stitch together journeys across multiple desktop and mobile devices to define the best Effective Reach in our campaigns.
Hyper-targeting doesn’t end with the use of Programmatic paid media buying. We also have awesome low-cost targeting options as audiences interact with our owned media like websites and emails. Whether it’s a B2C audience or B2B these enable us to deliver the best, most relevant content to nurture prospects along the path-to-purchase.
What is it? Real-time Programmatic advertising services
Using real-time technology to deliver the most relevant messages, offer and content for advertisers to maximise response from targeted consumers who are served display ads.
10. Agile optimisation to Marketing Excellence
The use of Digital marketing is now mature or reaching maturity in many organizations as suggested by the first chart in this report. This will be clear from how digital activities are planned and managed, for example, a more mature approach to digital marketing will be evident if a business has a defined digital channel vision and strategy with buy-in at a senior level both in the marketing organization and from business managers. The digital strategy will define clear goals, target audiences, and strategies for how to reach, convert and engage these audiences.
A mature use of digital marketing will also be evident in the process for reviewing and improving key digital activities. There will be a clear dashboard with defined KPIs that will be reviewed regularly in line with objectives set from shorter-term plans and review at a 90-day planning plus monthly and weekly level.
For example at Smart Insights we use this detailed channel dashboard (also available for Expert members) pulling data from Google Analytics for weekly review, enabling us to review month-on-month and year-on-year changes in performance in a way not possible with standard Google Analytics reports.
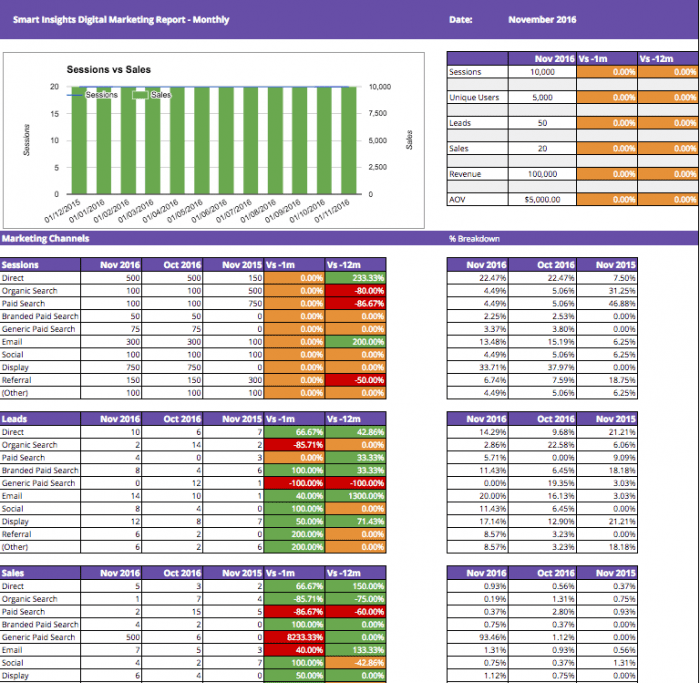
At a practical level, a business will have invested to create an effective website which is mobile optimised, will be active in social media on the channels relevant for their audiences and will have established programmes for reaching new prospects through the key channels such as search engine marketing, affiliate marketing, and online advertising.
In terms of personalized messaging, they will have Marketing Automation in place to deliver relevant, contextual messages to prospects and customers using Email marketing and CRM. These organizations will also have approaches to manage customer journeys between digital and offline communications and assisted sales or service channels such as Phone and Live Chat.

Download FREE Resource – Integrated marketing 2020 guide
How to integrate your marketing in just 10 essential steps. Our integrated marketing 2020 guide will step you through 10 success factors which leading companies are deploying today to future-proof their business by creating more effective, joined-up media investments and customer journeys.
Access the
Day 6. Digital Marketing plan template
Do you have an integrated digital marketing strategy? Our research shows that many businesses don't have a structured digital marketing plan, yet they are doing digital marketing. This popular template will give you a structure for applying the RACE framework to help you rapidly create an integrated digital marketing plan for your business.
Take a look inside: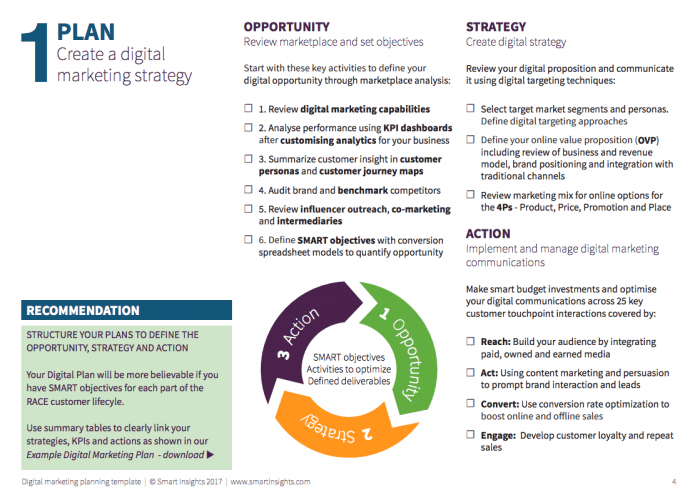
For the full Digital Marketing template detailing the activities across the RACE planning framework - download it here
Download FREE Resource – Digital marketing plan template
Our popular marketing planning template built on the Smart Insights RACE planning system.
Access the Free digital marketing plan template
Day 7. Social Media Marketing strategy guide
Create a plan to manage social media marketing to support your commercial goals.
Our guide is structured around PR Smith’s SOSTAC® Planning System to help you rapidly create or review a social media strategy in these 7 steps:
- Introduction: What is Social Media Marketing and Social CRM?
- Step 1: Benchmark and set business goals for your social media strategy
- Step 2: Create your social media strategy
- Step 3: Social listening and online reputation management
- Step 4: Define content and engagement strategy
- Step 5: Define communications strategy
- Step 6: Define approaches for the core social media platforms
- Step 7: Social media optimization (SMO)
Social media works best when it's part of an integrated E-communications strategy where Social media works together with Search, Email and Content marketing. Our social media strategy guide will help you create an integrated social media marketing strategy which shows you how to increase engagement to boost leads and sales using the social networks.
Take a look inside:

Social Media listening and online reputation management
90% of marketers say social media is important to their businesses but according to Social Media Examiner, only 41% are able to measure their social activities.
In this step, we cover how to put in place the people, process, and tools needed for effective listening. Score your brand now before we go through the details:
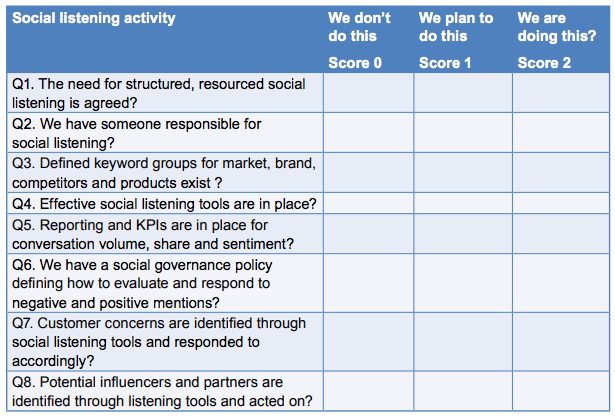
If you mostly score 2s, with some 1s, you have a good approach in place already. If not, there is room for improvement in how you use people, process and tools to listen and respond to online conversations. Read on to discover more on the tools and techniques.
Why social listening matters – convincing others of the need for social listening
‘Listen First!’ is the advice most social media consultants and agencies give when discussing the creation of a social media strategy. We agree! Improving the way you listen to conversations will help you through improving your insights on:
- Market understanding. Understanding issues that your prospects and customers discuss to identify types of conversations that are interesting to your audience. This way you can stimulate and participate in topics of interest and also feed into new product development plans.
- Brand mentions. How popular is your brand compared to competitors (share of voice)? Which issues are discussed around your brand? What is the ‘sentiment polarity’? This jargon means the proportion of positive to negative mentions compared to competitors.
- Negative comments. Managing and responding to negative comments about your brand.
- Sales opportunities. Identifying leads and sales opportunities – particularly important for social media marketing.
- Partner development. Following up on other types of comments to form relationships and participate in discussions.
- Product and service development. All of the above can help you understand customer needs.
Types of social listening
As well as social monitoring of a brand, or research of topics being discussed organically, there is also a third type of social listening; customer feedback. We’ve identified five different types of online customer feedback tools to help you select the right tool:
- Voice of customer website feedback tools and software. These provide a permanent facility for customers to feedback by prompts on every page, e.g. exit surveys or follow-up feedback emails such as Feefo or BazaarVoice.
- Crowd-sourcing feedback tools and software. Put simply, this is crowd-sourced structured social research. The example below from Uservoice shows how a brand asked selected customers to make recommendations of improvement to the brand.
- Simple page or concept feedback tools. Get feedback on a website or visual design concept.
- Customer intent-action tools. Assess the success and satisfaction with website visits.
- General online survey tools. These are surveys that you encourage completion through email marketing. For example www.surveymonkey.com
Take a look at our recommendations and then write a review of the tools that you have in place currently and those that you plan to implement in the coming year (as well as resource to manage).
A review of the three main types of social listening tools
1. Search engines
Great, simple, free tools for top-level analysis. Requires that a process is in place to extract the insights and set up the appropriate action.
- Free: Google Classic, Blog, Discussion, Alerts, Reader
- Free: Twitter Advanced Search
2. Social media monitoring and analysis
This type of listening tool varies a lot in terms of features and therefore potential uses. These tools generally offer some social research features as well as monitoring features meaning you can usually extract more value from them by tweaking the configuration.
- Free: Crunchbase, Social Mention, and Folllowerwonk are recommended for identifying the most influential
We have an infographic of a wide range of these tools.
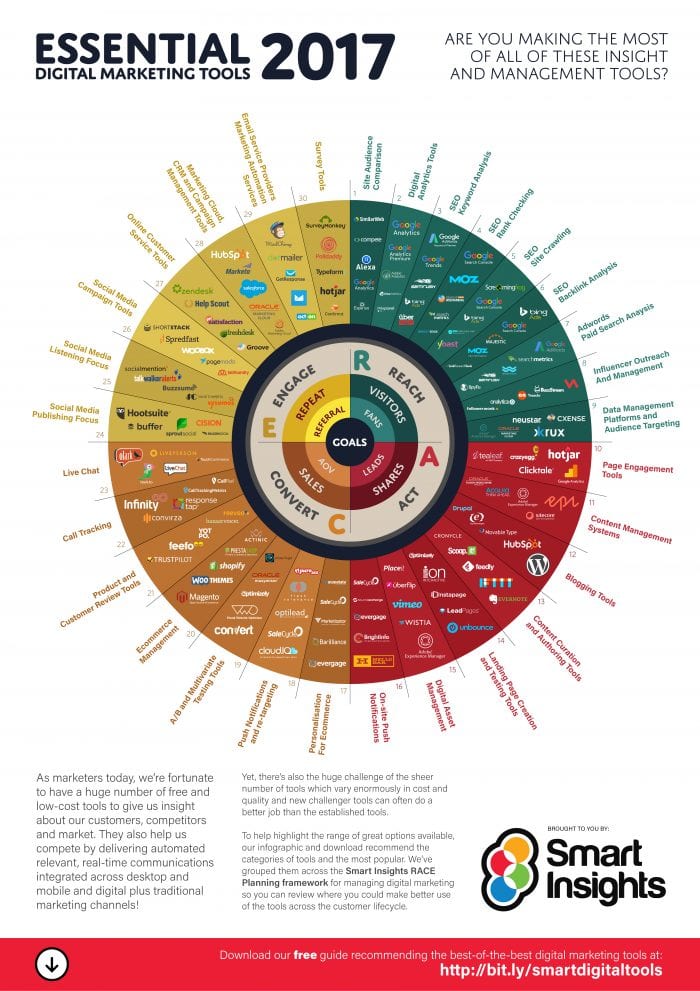
3. Customer communities
Currently, there are relatively few tools in this category. The two primary tools in this area are Uservoice.com and Userecho.com because they are based on crowd-sourced ideas and feedback, which is different to Kampyle, and the likes that are much more score
Paid: Uservoice, userecho.com
Paid Alternative: Kampyle
Selecting the right tool for you
Consider the following points before deciding which tool(s) is most relevant for you. Ensure when reading the items below you come back to your objectives/requirements.
- What’s included in the data sets? Does it cover blogs (via RSS feeds or crawlers), Tweets, Facebook likes, reviews, comments, forums, etc?
- What are the data sources and how does harvesting occur? Is the data taken from third-party providers or is the data collected in-house through a crawler (similar to the way that Google crawls the web).
- How is the data cleaned and prepared? What process does the provider go through to manage duplicates, spam, forum threads, etc.
- How is the data organized or segmented? How is the data being segmented so it contains the most pertinent consumer discussions around your specific area of interest?
- How is the data being analyzed and are actionable insights delivered? Is sentiment purely done by automated technology or by human analysis, or both?
- Can key influencers be readily identified? To decide how to escalate a negative mention you need to see how important the site is.
- How actionable are the insights and how should they be implemented? While data can be informational, consumer-generated media insights are the powerful building blocks.
- How much will it cost? What is the payment model for the service and there hidden costs?
Download Paid Member Resource – Social Media Strategy Guide
Understand how to best use social media in your marketing strategy as an individual or as a business.
Access the Social media marketing strategy guide
Day 8. Customer retention planning guide
In this guide, E-CRM specialist Andrew Campbell explains how to create a customer retention strategy using a range of frameworks and examples.
We think customer retention doesn’t get enough attention. Here are three cold, hard facts we present at the start of our retention guide explaining why customer retention is so important:
- It is 5-7 times more expensive to acquire a new customer than to keep an old one
- It costs a company $234 every time they lose a customer
- Loyal customers are worth up to 10 times as much as their first purchase

Developing customer-centricity
Effective retention marketers organize their entire business around the needs of their best
customers. To become customer-centric means:
- Developing a deep understanding of customer needs and behaviours
- Engineering a value proposition that meets customer needs and can be profitably
delivered by the organization
- Consistently delivering this proposition across all channels and touchpoints

The following table summarises customer-centricity and will help you pursue this goal as you design your retention strategy:
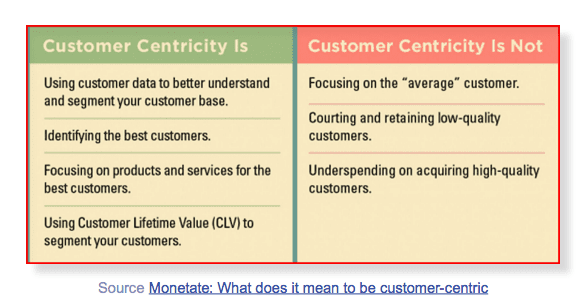
Give your ‘Best’ customers extra benefits which are highly visible:
Make it easier for them to buy from you e.g.
- Waive restrictions such as minimum order quantities
- Give them first options on opportunities such as discounted stock clearances
- Set up a dedicated website/portal/ordering system
Let ‘Best’ customers know you value them e.g.
- Invite them to special events, proactively check that they are happy or give them special gifts
- Reinforce their status and value in all communication with them
Ask for their opinions before making significant decisions e.g.
- Share your plans for a new product or brochure
- Let them rate the service they receive and raise complaints/issues
Make them feel special e.g.:
- Give key customers the opportunity to meet regularly to discuss important issues and enjoy networking opportunities
- Invite them to join a loyalty programme/club
Download business resource – Customer Retention Planning guide
Retain customers and grow your business with our retention guide.
Access the Customer retention planning guide
Day 9. 10 Business limiting SEO mistakes
Google's engineers have said there are at least 200 'ranking signals' which affect whether you can rank above your competitors or not for searches which will bring you new business. To make SEO even more challenging, many of them change frequently in Google's algorithm updates.
Take a look at our guide:


Limited measurement of organic search
Organic search is a key driver of website traffic for many sites and yet this is not always measured or tracked effectively. Organic search is just one of many different channels, each of which should be assessed against higher level objectives, goals, and KPIs.
The creation of a measurement framework will enable you to structure performance reporting so that organic search – and other channels – are measured against the broader goals you’re aiming to accomplish as a marketer. Clarity around SMART objectives linked to goals and KPIs will give you the ability to prioritize activity, identify tools (such as Google’s Search Console for granular data) and report on performance.
The Smart Insights RACE planning framework can be used to simplify and articulate measurement and reporting by considering the key online marketing activities that need to be managed as part of a digital marketing strategy:
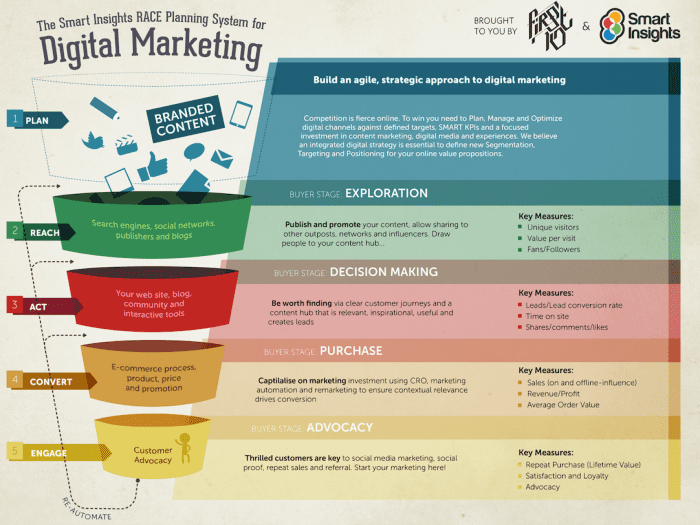
As can be seen in the graphic above, RACE looks at metrics at each stage of the purchase funnel and takes into consideration the VQVC elements covered in the previous section.
RACE is a useful way of thinking about your goals and measuring effectiveness for SEO since although it drives Visitor volume in the Reach phase, we also need to think about the Quality and Value of visits generated:
- 1. Reach – building brand awareness by maximising reach
- 2. Act – encouraging interactions to generate leads
- 3. Convert – conversion to sale
- 4. Engage – developing long-term relationships to build customer loyalty and repeat purchases

Weak external link-building strategies
Gaining quality backlinks from other relevant sites remains the number one ranking factor for SEO success. There is no shortcut to success (as demonstrated by the Smart Insights example above) and if a site wants to compete effectively with competitors in their sector or niche, quality content is king.
Key techniques for link building:
- Article Marketing
- Blended or universal search
- Directory marketing
- Index Inclusion
- Internal linking strategy
- Local SEO
- Mobile SEO
- Multilingual SEO
- On-Page optimization
- SEO analytics
- SEO content strategy
- SEO strategy
Rand Fishkin of Moz talks about the shift from link building to link earning because gone are the days when links to websites could be easily acquired. If your site does not include content worth linking to, you have to find a way to earn links in the right way.
An effective outreach programme should work collaboratively with PR, marketing, sales, and SEO to create and promote content that adds genuine value for users in exchange for relevant links that will help create what’s referred to as a natural inbound link profile.
Download FREE Resource – 10 business-limiting SEO mistakes
The search engine optimisation (SEO) mistakes to avoid and what to do instead. Google's engineers have said there are at least 200 'ranking signals' which affect whether you can rank above your competitors or not for searches which will bring you new business. To make SEO even more challenging, many of them change frequently in Google's algorithm updates. So, it can be really tough knowing what matters in SEO and what doesn't.
Access the
Day 10. Customer persona guide
This guide (powerpoint presentation) shows examples and good practices to help you create better marketing personas and customer journey maps.
Take a look inside:

Our customer persona guide includes detailed checklists, models and frameworks that can be applied to your business, strategy recommendations, examples of general marketing personas and much more!

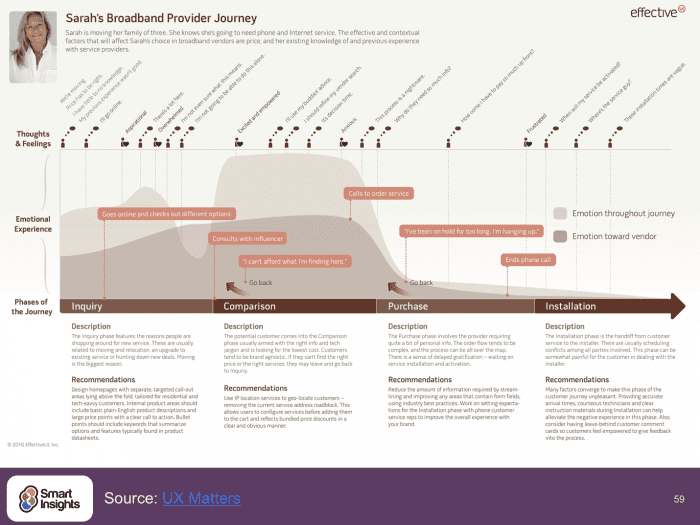

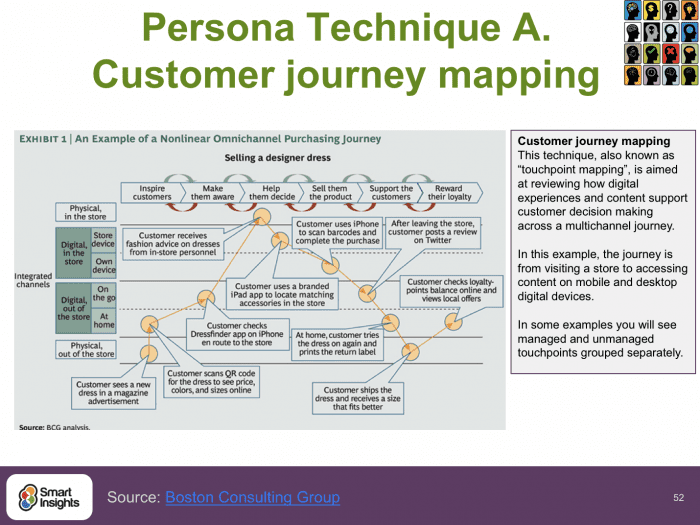
Download PremiumResource – Customer Persona Guide
Examples and good practices to help you create better marketing personas and customer journey maps.
Access the Customer persona guide and template
Day 11. Email Trends 2018: A visual guide
How will this report help me and my business?
Email marketing is still worth taking seriously. The aim of this guide is to showcase some of the latest Email marketing and marketing automation techniques deployed by brands to engage their subscribers and develop purchase intent. It pays to keep up-to-date with the latest approaches to email marketing techniques given its importance to all types of business.
In 2018, Email Marketing is one the most effective techniques for digital marketers, so keeping up-to-date with the latest trends in the industry is super important. Our recent research on the State of Email marketing in 2017 with partners GetResponse showed that marketers rate email marketing one of the most effective digital media channels
Take a look inside:

Download FREE Resource – Email trends 2018: A visual guide
Review your approach to email marketing by reviewing the latest trends.
Access the
Day 12. landing page conversion guide
Learn best practice for higher-converting B2C and B2B Landing pages.
This guide is an in-depth 30,000 word, 106-page A4 page PDF Ebook with over 50 examples, recommendations, and best practice checklists.
Take a look inside:
Factors you control to improve landing page performance
Here are some of the main characteristics of the page you control, that we will drill down into later in the guide:
- Relevance of the page. In the first few seconds of a visit this is affected by the relevance of the header of the page (images and copy) to the context of the user’s visit - why and where have they arrived from?
- Length of the landing page. There is a popular myth that short-form landing pages are ‘best practice’, with key content and call to action above the fold. However, there is sufficient evidence to counter this view and demonstrate that the length of a landing page should be determined by a mix of factors, including the needs of the audience for detailed information. We discuss this in more detail in Step 4 – Create the optimal page layout.
- Placement of call to action. All calls to action must be above the fold right? Wrong. Yep, surprising isn’t it. In truth, there is no hard and fast rule. Whilst it’s true that in most cases a strong call to action above the fold increases conversion, there are cases where this isn’t true and actually putting the call to action in front of the customer before they are ready to take action can actually put them off. We also discuss this in more detail in Step 4 – Create the optimal page layout.
- Matching content to marketing creative. This is marketing good practice 101 – make sure that your landing page is consistent with the source marketing campaigns that generated the visit. Often referred to as the ‘scent trail’, this ensures visitors know they have landed on the right page because they can recognize the creative treatment. We discuss this in more detail in Step 5 – Compelling content and creative.
- Consistency of messaging. This is closely related to marketing creative. It’s important that you replicate the headline copy from your marketing campaigns on the landing pages. This is especially important for paid search where search engines like Google will look to see if the keywords used in ad copy match content on the destination page – failure to do this can adversely affect ad Quality Score. We also discuss this in more detail in Step 5 – Compelling content and creative. þ
- Form validation. Forms are typically used by B2B marketers on landing pages, for a variety of reasons including capturing contact information from people downloading free content. The biggest barrier to goal completion is poor user experience, where the landing page makes it hard for the visitors to quickly and easily complete and submit the form. We discuss this in more detail in Step 3 – Engaging your visitor.
- Optimal blend of content. Let’s be realistic – if you have a large audience, it’s almost impossible to design a landing page that is perfect for everyone (we’re yet to see that so please do share if you have one!). This is where landing page optimisation comes into playtesting different variations of the landing page to find out which one drives the best results (based on the KPIs you are measuring performance against). We discuss this in more detail in Step 7 – Improving results.